Unleashing the Power of OSINT. Google Dorking: Unveiling Hidden Treasures of the Web.
Google Dorking is a technique that leverages advanced search operators in search engines like Google to uncover specific, often hard-to-find information. By using carefully crafted queries, users can retrieve data not typically accessible through standard searches. This method is widely used for penetration testing, information gathering, competitive analysis, and cybersecurity research.
Intro
Have you ever heard from someone that it is hard to find information about a particular topic or person or that they were unable to find something on the World Wide Web?
Accessing information is as easy as a few clicks. As search engines like Google, Bing, Yahoo!, Yandex, and much more act as gateways to the vast expanse of the internet, it’s natural that everyone (mostly) is seeking new methods to enhance their searching capabilities. “Google Dorking” is one of those methods that you can use in your daily life.
Understanding Google Dorking.
So… Google Dorking refers to using advanced operators in Google’s search engine to locate specific information that may not be easily discoverable through conventional search methods. Google searches are basically search queries that can unfold specific information.
Main purpose of Google Dorking
Google Dorking could be used for various purposes, including penetration testing, information gathering, security research, finding information about a particular person (which could be used in social engineering attacks), and so on.
Advantages of Google Dorking
Information discovery. Google Dorking lets us discover information that is not easily accessible through regular searches.
Example: Let’s say you work in the cybersecurity field and want to find publicly accessible documents containing information about “Hive RaaS.” For this, you could use a query like:
1
“intext:Hive RaaS” — this query instructs Google to search for web pages that contain the exact phrase “Hive RaaS” in their content.
You can also refine your search by adding additional dorks like:
1
“filetype:pdf intext:Hive RaaS” — this query narrows down results to PDF files that mention “Hive RaaS”.
Research and analysis. Competitive intelligence.
Researchers and analysts can leverage Google Dorking to discover specific data related to a particular topic of interest.
Example: Your company is trying to conduct market research to get insights into industry trends, customer preferences, or what competitors are doing and their strategies. Using specific industry-related terms and products, you can uncover relevant articles, reviews, or social media mentions. For this, you could use query like:
1
site.com “industry trends” OR “customer preferences” or “product reviews” — this query instructs Google to search for web pages within.com domains that contain any of the specific phrases, such as “industry trends”, “customer preferences,” or “product reviews”.
You can also further customize query by adding specific industry-related terms or product names relevant to your market research.
These are only a few examples of Google Dorking and how you could use it ethical way if you respect privacy, legal boundaries.
Real life example of Google Dorking
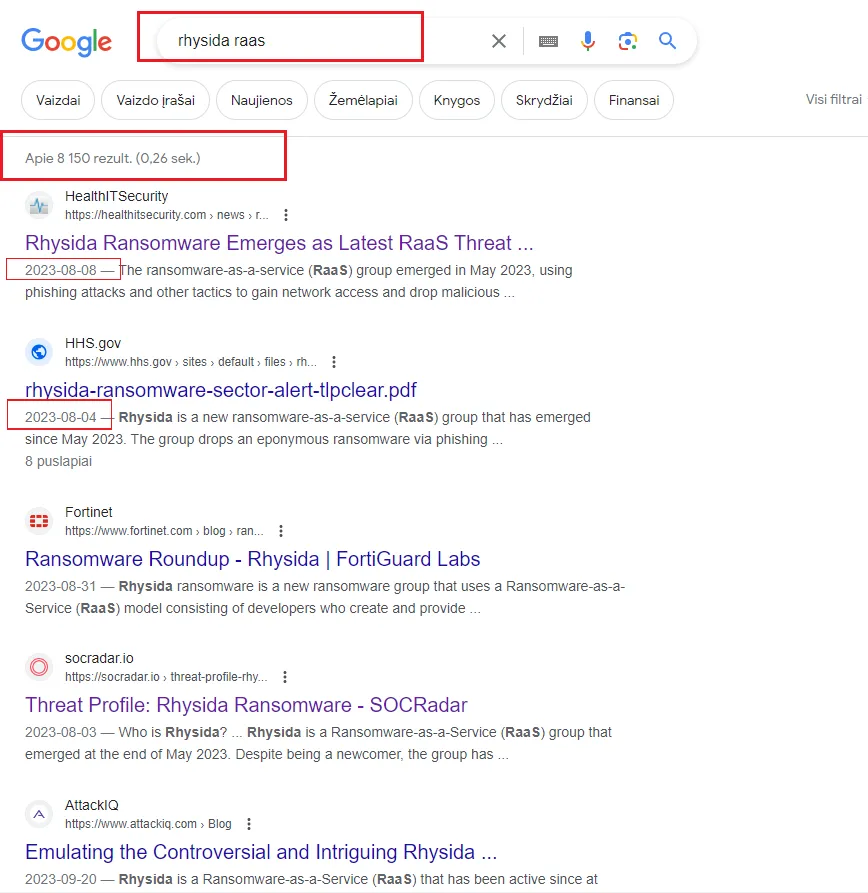
Soo…. I wanted to find more information about, let’s say, Rhysida RaaS. A basic Google search would look like this:
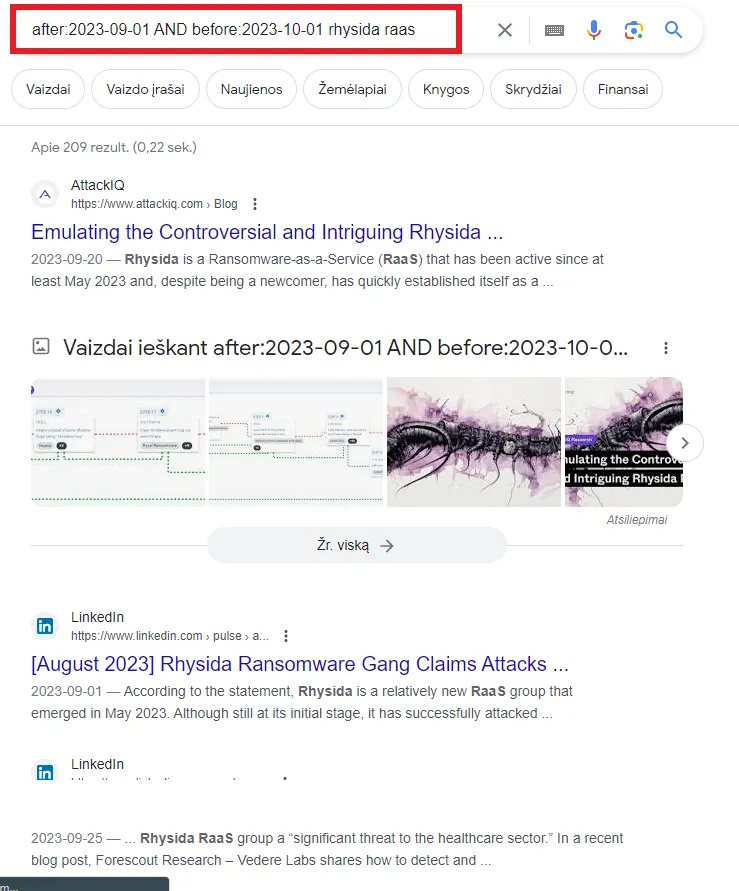
My search found what I wanted, but we are searching for more recent posts. Here is where Google Dorking comes in.
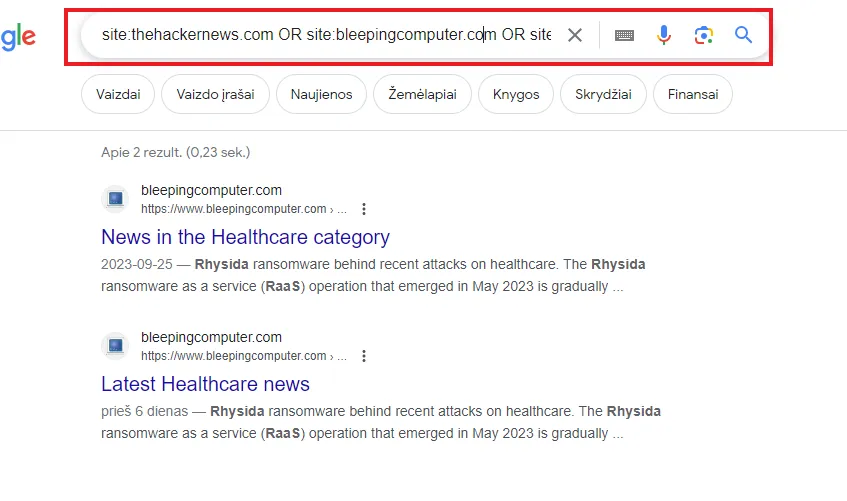
This query helps a bit, but we can add a few more things, like adding site:webpage, to our query.
As you see, we narrowed down from 8150 results to 2 results.
My most used Google Dorking queries
Shows only those pages that contains exact word or statement.
1
“Context”
Only retrieves information from website that you mentioned with exact context.
1
site:website “Context”
Only searches for PDF file with exact title content that you provide.
1
filetype:pdf intitle:”Context
Only searches for PDF, DOCX, PPT files that have exact context that you provide.
1
filetype:pdf OR filetype:docx OR filetype:ppt “Context”
Only searches in given Social Media platforms exact context that you provide.
1
site:SocialNetwork | site:SocialNetowrk2 | site:SocialNetwork3… “Context”
Only searches for given context after and before given date.
1
“Context” after:YYYY-MM-DD AND before:YYYY-MM-DD
Searches given websites for given context after and before given date.
1
site:Blog | site:Blog2 | site:Blog3 after:YYYY-MM-DD AND before:YYYY-MM-DD “Context”
Shows the website homepage even if website is down.
1
cache:website